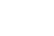Email Encryption. How to send and receive an encrypted email?
Email encryption involves encrypting, or disguising, the content of email messages to protect potentially sensitive information from being read by anyone other than intended recipients. Email encryption often includes authentication.
Email is a vulnerable medium, especially if the emails are sent over public Wi-Fi networks which are unsecure and hackers who gain unauthorized access to an email account can access attachments, content, and even hijack your entire email account. So, it’s always recommended to use email encryption while sending sensitive information, such as login credentials, bank account numbers or Social Security numbers.
How email encryption works
Encryption is no more than scrambling up the contents of a message so that only those with a key can decrypt it. It simply sorts of like those puzzles we did in school where every letter of the alphabet had to be converted to some other letter of the alphabet to decode the final message. Computers make the scrambling far more complex and impossible for a human to crack by hand. When you encrypt an email, its contents are scrambled, and only the intended receiver can unscramble it with the key.
Public Key for encryption
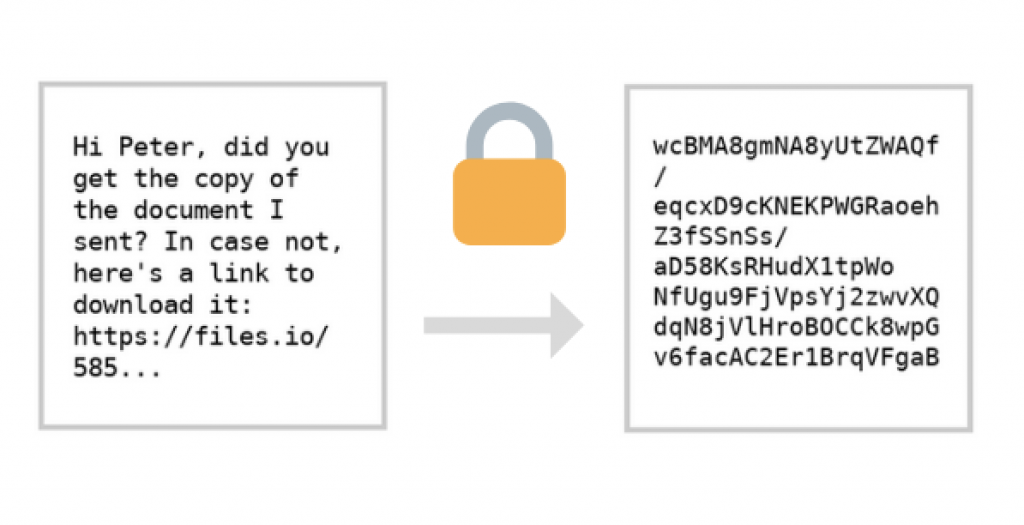
Email encryption uses something called public-key cryptography. Each person has a pair of keys, the digital codes that are used to decrypt an encrypted message. Your public key is stored on a key server where anyone can find it, along with your name and email address. Conversely, you can find other people’s public keys on keyservers to send them encrypted email.
To encrypt an email, use the recipient’s public key to scramble the message. Due to the technology behind this type of cryptography, the public key cannot be used to decrypt it. The email can then only be decrypted by the recipient’s private key, which is stored somewhere safe and private on his or her computer.
Digitally Signed Emails
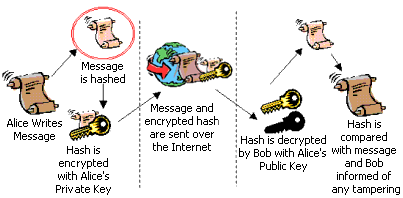
Digital Signature is a process that guarantees that the contents of an email have not been modified in transit. When users receive your email, they will see a message that the email has been digitally signed. It means that a one-way hash (encryption) of the message content is added using your public and private key pair.
The client can still read it, but the process creates a “signature” that only the server’s public key can decrypt. The client, using the server’s public key, can then validate the sender as well as the integrity of email contents. Whether it’s an email, an online order or a watermarked photograph on online commerce, if the transmission arrives but the digital signature does not match with the public key in the digital certificate, then the client can find that the message has been altered.
How to send an email digitally signed
Microsoft Outlook 2013, 2016
To Sign an Email Message, simply click the Sign button that now appears on a Compose Message email dialogue under the Options tab.
Mozilla Thunderbird
Select the Security icon appearing in the Write message window. You can Encrypt or Digitally Sign messages by selecting either or both options.
Mail sent with a digital signature will show as digitally signed by the sender to any receiver of that email.
Apple Mail
Open a new message. Two icons will be available, a small lock icon and a digital signature icon. Click the digital signature icon to send a digitally signed email. The recipient will receive the message as a digitally signed email.
Sending Digitally signed emails vs Encrypted Emails
To exchange secure (encrypted) emails with someone, there are some additional steps required. To Encrypt an email Message, you will need to provide your public key to the party you wish to encrypt for, and vice versa.
The recommended way to do this exchange is to send the other party a Signed email to exchange keys.
1. Open a new message to send to the contact with whom you wish to exchange public keys. Ensure the message is digitally signed (but not encrypted) and hit send. You will be prompted to Allow for your public key to be sent upon sending the email. Select Allow.
2. You will need a copy of the recipient’s public key to exchange Encrypted email. Have them send you a digitally signed email. After receiving the digitally signed email containing a copy of the other person’s public key, Outlook will store the public key. Upon opening the email you will be prompted again. Select Allow to obtain a copy of the public key is sent to you.
3. You can make sure the recipient’s certificate and public key have been stored by clicking on Certificates in their contact profile.
4. Click Save and Close.
Off-the-shelf encrypted email client
There are a lot of email apps out there that claim to offer end-to-end encryption, but many contain security vulnerabilities and other shortcomings. Do your research before choosing an off-the-shelf secure email app. Below is a list of some of the best Off-the-shelf encrypted email clients.
- ProtonMail
- Tutanota
- Hushmail
- Countermail
- Runbox
- Kolab Now
- Mailfence
- Posteo
- StartMail
- Mailbox
- PreVeil
- Zoho Mail
Let us see some of the encrypted email clients in detail.
Tutanota
Tutanota is an encrypted email provider from Germany. They position themselves as a secure alternative to Gmail. According to their website, they are also planning to include a calendar, notes, and cloud storage in their offering – and of course, all of these features will be encrypted too.
Tutanota is one such secure email service, with apps for mobile and a webmail client. It even encrypts your attachments and contact lists. Tutanota is open-source, so it can be audited by third parties to ensure it’s safe. All encryption takes place in the background.
ProtonMail
A mature end-to-end encrypted email service with excellent mobile apps.
ProtonMail’s servers are locked down under 1,000 meters of granite rock, in a Swiss bunker that can survive a nuclear attack. And its digital security is about as impressive. It began development by a team of CERN Large Hadron Collider scientists in the wake of the 2013 Snowden leak and has since become the #1 most-used secure email service with over five million users.
ProtonMail is designed with the principle of zero access and zero-knowledge, which means that the email servers and staff that work with them have no way of reading or sharing your emails.
Based in Switzerland, ProtonMail data is protected by the Swiss Federal Data Protection Act (DPA) and the Swiss Federal Data Protection Ordinance (DPO), which offers some of the best privacy protection in the world. In the unlikely case, ProtonMail was ordered to hand over user data, it would have to be specifically subpoenaed by the Cantonal Court of Geneva or the Swiss Federal Supreme Court. And, even if user data were seized, it would be impossible to decipher because of ProtonMail’s encryption.
Checkout our dark web links to know more.